The topic “Crisis of Fund Management” consists of three important words -Crisis,fund and management. Now, let me conceptualise the term “fund” first.
(1) Fund : The term “fund” is defined differently in different topics of financial Management.The term “Fund, used in working capital management can not be construed as an equivalent to the fund used in fund flow statement for financial statement analysis. The term fund has been used to indicate the quantum of liquid cash available at any point of time either in iron-chest or in bank account as the case may be. It is true that higher the liquidity, lower the risk and obviously lower the profit as profitability and risk are corelated. Some relaxation has been made by including the inventory or value of stock into the fund.
(2) Management : The fund management and cash management are not the same thing. The main focus of Cash management is to receive and utilise the cash in the befitting manner in Govt Undertakings- this aspect is well known even to be a layman. Usually, a budget is prepared and it is approved by the Govt. The Expenditure is incurred,bills received,it is passed for payment and the payment is made through Reserve Bank of India. The Govt accounts are not Constitutionally supposed to accrue interest. That is why it does not matter whether the idel cash is kept in current Account or in savings account or in short term fixed deposit. What is most important in this case is that the Govt should get the money as and when approached. This fund management technique is mostly imported by the PSUs and the autonomous body as most of the Heads of those organisations belong to the bureaucracuy of the Govt. On Analysis, it may be seen that the PSUs and autonomous bodies are loosing crores of rupees for this faulty cash management system or fund management system.
(3) Crisis : Slight touch is evident as to the crisis of fund management surfaces during the fund management in PSUs. The basic Crisis generates in the suystem itself. It is seen from the financial reports,balance sheet,statement of accounts or budget speech that considerably, a larger quantum of idle cash is lying in current Account or in iron chest of PSUs for years together without earning any interest thereof though the quantum of interest earned could have solve reasonably the problem of shortage of fund in the PSUs.
Another crisis is revealed in the management of retained earnings. It is interesting to note that some Central Govt Undertakings are not maintaining the Commercial Accounting procedures so far the treatment of Depreciation fund is concerned. In some cases,it is revealed that though Depreciation is charged in Profit & Loss Account, the same is not being invested or utilised in a well -stipulated way so that the accumulated sum can jolly well meet a bigger portion of demand for fund for replacement of plants and machineries of the PSU’s are going to be out of order,antidated and obsolete. In some cases the capacity is reduced to nil, operational and maintenance expenses are going high. The management is equivocal for modernisation but the fund created by charging against the Profit & Loss A/c can hardly be available at the nick of time. This simply speaks the crisis of fund management arising out of non-professional fund management.
The third point of crisis is noticed in lack of proper store management and the unwillingness to realise the receivables at or before the expiry of Credit period.As a matter of fact,most of the PSUs are to work against advance.In this case the net working capital is negative(-) as CL > CA but in practice, it is seen that the position is reverse. Most of the PSU are not suffering from order to supply or manufacture but they are suffering from inadequate production and lesser marketability. This has been aggravated by the high overhead expenditure, mostly because of overtime allowances and existances of large nos of high salaried persons in the top level. In this way, if i go on writing differnt facets of crisis, the work will be voluminous in nature. So to concentrate on the topic we have to find out the core of crisis.
See more at http://www.findtutoronline.net/blog
Suggestions & feedback are most welcome.

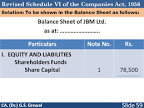
Balance sheet is a summary of balances which showed Liabilities side as well as Asset side. I discovered a formulae at my Own level to make it meaningful & memorise the same for Mba’s/CA’s/CMA’s & also Under Graduates commerce level.
On liability Side : S R Sen Under Control OF Police
On Asset Side : Five Indian Cultivators Looking A Melody
Each Alphabet first letter denotes the Heading of Balance sheet of both Assets & Liabilities which is mentioned below :
On Liabilities side :
S–Stands for—-Share Capital–Equity Shares-Authorised,Subscribed,Issued & paid up, Preference shares will come under this Head.
R–Stands for—-Reserves & Surplus—General Reserves,P&L Cr. balance,Share premium,Capital Reserves etc will come under this Head.
Sen—Stands for ——–Secured Loans—-Loans against mortgage of Fixed Assets.
Under— –Stands for ————-Unsecured Loans—–6% debentures
Control—Stands for——Current Liabilities—Sundry Creditors,Bills payable,Outstanding Expenses etc.
of
Police ——Stands for ——Provisions for Taxations,Proposed Divident, Provision of Taxations etc.
On the Assets Side :
Five—-F stands for—-Fixed Assets—Land & Building,Plant & machineries,Car,Patents & copywrights,Furniture & fixtures,Goodwill etc
Indian—I stands for—–Investments- Purchase of Nationals savings certificate, Purchase of IDBI Bonds etc.
Cultivators—C stands for—-Current Assets———-Sundry Debtors,Bills Receivables,Inventory,Cash in hand, Cash at Bank etc
Looking ——L Stands for—Loans & Advances——Stafff Salary Advance, Advance Rent, Loans given to Outsiders etc.
A——stands for—-All Advances
Melody—M Stands for —-Miscellaneous Expenditure——Premilinary Expenditures. Discount on Issue of Shares,Advertising Suspense etc.
See more at : http ://www.findtutoronline.net/blog
Suggestions & feedback are most welcome.
r project
Introduction: This project contain exploratory data analysis using r and Ggobi sofrware. r software is more powerful tools for analysis the data. Using this we can analyze all kind of descriptive and statistical inference. Addition to this also we can use model like regression analysis.
In this we used employee data for analyzing the salary of associates. The salary of associates depends on so many factors. In this data we included variables are education(in years), salary begin, Previous experience (in years), Job time, minority.
The statistical tools used,
1. Mean, median, Mode
2. cross tab analysis
3. Scatter plots
4. Correlation Analysis
5. Regression Analysis.
The below is the list of r option we used
|
R option
|
Uses
|
| read.table() |
To read employee text file |
| attach() |
To get attached all variable into r console |
| colnames() |
To list the name present in employee data |
| summary() |
To get the descriptive statistics like Minmum, maximum, 1st quarter, 3rd Quarter, |
| plot() |
To plot the scatter plot |
| pairs() |
To plot the scatter plot including all variable together |
| tables() |
To do the cross tab analysis |
| cor() |
To perform the correlation Analysis between two variables |
| lm() |
To perform the linear regression. |
#To read the text file into R console we used read.table option.
Emp=read.table(“D:/CARS/Project-cars/Ranadeeb/emp.txt”,header=TRUE)
# Attach the tables imported we need to use attach option.
#Once we attach option used, then we can give Individual variable name for analysis
#and plotting the graph.
attach(Emp)
#To find the column names we need to use the colnames() option. This will display
the column names of the attached file.
colnames(Emp)
#The variables prsent in the emp data are
#1. Educ ( this is the number of years of education)
#2. jobcat ( this will measure the category of job they are doing. 1 reprsent
#trainee. 2 will reprsent Team Members. 3rd will reprsent Manaager Level.
#3. Salary
#4.Salbegin (this salary when started job first time)
#5.Jobtime
#6. Prevexp (It is the experience of the candiates)
#7. Minority (0 means no and 1 means yes)
#The summary will give the overall descrptive statistics for all quantitative data.
#The descrptive statistics are given below.
#1. Minimum Value: This will give the minimum valve for the given data.
#2.1st Qu: the first quarter the 25th percentile data.
#3.Median:It is the middle value of the data set when data is arranged in either
#in ascending or descending order.
#4. Mean: It is the sum of the observation divided by total number of observation.
#5. 3rd Qu: this will give the 75% of the data.
#6. Max: It will give the maximum valuve of data set.
summary(Emp)
summary(salary)
# To get the cross tabulation we can use table option. this will give the cross tabunlation of jobcategory versus minority.
table(jobcat,minority)
# To plot the scatter plot we can use the command plot(x1,x2).
plot(salary,salbegin)
# there is a postive correlation between salary and salarybegin.
# AS salarybegin is high then salary of current also be high.
plot(educ,salary)
#when we plot the correlation between educ and salary, there is a posstive correlation
#between these two variable.
plot (educ,salbegin)
# there is a postive correlation between education and salary of begin.
#To combinaly see the all the correaltion using scater plot, then we can use pair option.
pairs(Emp)
#to calculate the correlation between all variable then we can use cor option.
#the correlation is the degree of association between two variable.
# The correlation is classfied into three types.
#1. Posstive correlation (Where correlation is close to one)
#2. Negative correlation (where correlation is close to – one)
#3. Zero correlation ( where correlation is close to zero)
cor(Emp)
#As the name suggests, in simple terms correlation is the relationship between 2 variables.
#Correlation is defined as the “degree of strength of association between 2 variables”.
# Here 2 variables, does not mean 2 values in the same variable, but two different variables.
# Correlation explains the degree of the relation the 2 variables share among themselves, but does not explain the cause and effect of each other.
#Usually, correlation is required to be found between at least one dependent variable and another independent variable
#and its relation or association on the dependent variable.
#The researcher looks at things that already exist and determines if and in what way those things are related to each other.
#The purpose of doing correlations is to allow us to make a prediction about one variable based on what we know about another variable.
#Correlation co-efficient is denoted by small r . Always co-efficient of correlation value r ranges between -1 and +1.
# To find out the correlation, we usually do a scatter plot of both x values (independent variable) and the y values (dependent variable).
#A correlation tells us that the two variables are related, but we cannot say anything about whether one caused the other.
#This method does not allow us to come to any conclusions about cause and effect. Correlation is not Causation!
#regression Analysis
#Regression is said to be said an extension of Correlation.
#Regression is the “Functional relationship between dependent and independent variables”.
#Regression gives you the cause & effect relationship of the variables which is left incomplete by Correlation.
#We regress the pattern of the future occurrence of the variables based on the actual prior values.
#Regression forms a basis for future estimating & Forecasting while taking into account #the cause & effect of the relationship of the variables.
#Definition:- Regression analysis is the process of constructing a mathematical #/statistical model or function that can be used to predict or determine one variable by #other variables.
#Regression involves two or more variables in which one variable is predicted (called the dependent variable) and designated as Y,
# The variable/s which help the prediction are called Independent variables or #Explanatory variables and are designated as x1 x2 x3 …. xn.
#The values of x variables will be known or have actually happened, based on which we will be predicting the Y variable.
#Here, only a straight line relationship between the dependent and independent variables is assumed.
# regression analysis was carried out for employee data
# dependent variable is salary and Indpendent variable is salary_begin, Education, #Previous_Experience.
lm(salary~educ+salbegin+prevexp)
#The above model used to run the linear regression of salary as the dependent variable #and education, salary begin and previous experiance was considered as a indpendent variable. The model shows that,
#salary=-3.661.51+735.956*educ+1.1749*salbegin-16.730*prevexp
This 9 Step On-Page Search Engine Optimization Guide will help you optimize your website pages, so they will have the best chance to get found by your target market. The Guide outlines the most important factors to consider when optimizing each page on your site. These steps are listed based on importance, so don’t skip a step. Also, remember that creating new optimized content on a weekly basis is critical to achieving long-term success with SEO.
Step 1: Choose Keywords
Read the page’s content and identify two (2) keywords that are most relevant to the overall page content. Choose one (1) primary keyword relevant to the page’s content and one variation of that keyword (e.g. plural variation or two closely related keywords) per page. If you can’t identify one primary keyword for a page, you’ll need to create new website pages to separate the different content. If it’s not clear to you what page is about, then your visitors and the search engines won’t be able to understand the page either.
Step 2: Page Title
The page title appears as the blue, bolded, underlined text on a Google search results page, and also on the top left the browser bar. The page title should follow these guidelines:
Be under 70 characters with no more than two long-tail keywords per page title
The primary keyword should appear first
Each keyword phrase should be separated by pipes (|)
Each page title on your website should be unique
Except for your homepage and contact us page, each page title should NOT include your business name
Step 3: Meta Description
The meta description appears on a Google search results page under the Page Title. The meta description helps people decide whether to click on your result, or a result above or below you. Think of it as a call to action. The meta description should follow these guidelines:
Be under 150 characters (but not under 100 characters; take advantage of the space you have)
Incorporate the primary keyword and at least one secondary keyword
Provide a valuable, compelling reason for why someone should visit the page
Include keywords in a conversational format; don’t just cram in keywords for the sake of listing them
Step 4: URL
The website page’s URL should include the primary keyword. Each word in the URL should be separated using dashes (-). e.g. www.examplesite.com/inbound-marketing-software
Step 5: Heading Tags
The page should have one H1 heading tag that incorporates the primary keyword, and should align with the page title and the URL or the page. This H1 tag should appear at the top of the page and should be the first thing people see when they arrive on a page.
Step 6: Page Content
Use your primary keyword a few times throughout the page’s content. Don’t overthink keyword density or placement, you should mention them naturally. Try to bold or underline the keyword at least once. This has an effect on how relevant the keyword is to the page. Also mention the secondary keywords when you can.
Step 7: Add a Call to Action
Every website page, including your blog, should have at least one call to action above the page’s fold (Don’t make your website visitor scroll down to see the call to action). Calls to action can help SEO by creating an internal link on your website to a specific landing page. Most calls to action are images; therefore you can optimize the image filename and alt text for the primary keyword you’re targeting on the page (see step 9).
Step 8: Internal Links
If you mention the primary keyword of this page on other pages within your site, then link to this page using the primary keyword as the anchor text. For example, you should link to a page about inbound marketing software using the anchor text “inbound marketing software.” To make sure this is completed, take a moment to create one (1) or two (2) links on related pages that link back to the page you’re optimizing.
Step 9: Images
Any images used on the page should be optimized so that search engines can “read” the image. Optimize the most prominent image on the page using the primary keyword, and then use the primary and secondary keywords for any other images. Images can be optimized in two ways:
File name: Each word should be separated with dashes (-), e.g. inbound-marketing-software.jpg
ALT text: The alt text should match the file name, without dashes, e.g. Inbound Marketing Software
If you are unable to change image file name or if it’s too time consuming, then only change the most prominent images’ alt text using the primary keyword.
Meta Keywords
They aren’t part of Google’s or Bing’s search algorithm, so I’m not including them as a step. However, still use your primary and secondary keyword in the page’s meta keywords. Smaller search engines still might use them in their algorithm, but major search engines do not use them. HubSpot does not recommend you optimize your meta keywords.
Repeat these 9 steps for each of your website pages.
See more at : http:www.findtutoronline.net/blog
Suggestions & feedback are most welcome.
Strategic Purchasing Procedure : Procurement Under Supply Chain Management :
_____________________________________________________________________
Purchase procedure for Procurement in Regions/ Branch Offices
and Head Office except for Works & EFS.
All our business activities involve purchases of various items & services from different vendors.
In order to ensure that we buy from a qualified source at competitive prices, this procedure is laid down. Continuous evaluation of the vendors for quality, reliability & cost effectiveness is the key issue addressed in this procedure.
The basic issues included in this procedure are as follows:
- Selection & approval of vendors
- Evaluation of offers & negotiations
- Terms & Conditions of purchase
- Vendor appraisal.
The procedure is applicable to all divisions except for Works and Engineering and Field Services (EFS) for whom separate procedures are laid down.
As a part of process improvements we have amended the procedure & list of amendments is enclosed.
This procedure comes into force with immediate effect.
Encl
Table of contents
- PREAMBLE: 3
- SELECTION & APPROVAL OF VENDORS: 3
Inclusion of New Vendors in Approved Vendor List. 3
ISO approved vendors. 3
Client/ Consultant/Preferred Vendors. 3
Dealers, Stockists and Traders. 3
Vendors of Foreign Origin. 3
Other Category of Vendors. 4
Dormant Vendors. 4
- ENQUIRIES.. 4
- EVALUATION OF OFFERS.. 4
- NEGOTIATION.. 4
Terms & Conditions of Purchase: 5
- PURCHASE ORDER.. 5
Placement of purchase order. 5
Amendments to PO.. 5
Methods of Purchase. 6
Order Acknowledgement: 6
Siemens Equipment: 6
Proprietary & Consumable items: 6
Processing by vendors: 7
Adjustments of Payables/ Receivables: 7
Liquidated Damages: 7
Penalty: 7
Warranty: 7
Deviation: 7
Post order contractual problems: 7
- INSPECTION, APPROVAL AND PASSING OF BILLS: 7
- RATE CONTRACTS.. 8
- VENDOR RATING.. 8
- PERFORMANCE AT SITE: 8
- REASSESMENT AND/OR DELETION OF VENDOR: 9
- BLACK LISTING: 9
- BUSINESS CONSULTANTS AND / OR CONTRACTORS.. 9
- SAFETY & ENVIRONMENTAL REQUIREMENTS.. 9
- DEPENDENCY RISKS FOR OUTSOURCING.. 9
Annexures No of Pages
Annexure I Vendor Information Form 3
Annexure IA Vendor Master Maintenance Form 3
Annexure II Essential category of Vendors for Evaluation 2
Annexure IIA Vendor Evaluation Report For Manufacturers 3
Annexure IIB Vendor Evaluation Report For Service Providers 3
Annexure IIC Vendor Evaluation Report For Civil Contractors 3
Annexure IID Vendor Evaluation Report For Engineering Services Providers 2
Annexure III Commercial Terms And Conditions For Purchase 1
Annexure IIIA Commercial Terms And Conditions For Service 2
Annexure IV Quotation Evaluation Sheet 1
Annexure V Visit Report 1
Annexure VI Minutes of Meeting 1
FINANCIAL MODELLING
Financial modelling refers to performing a set of calculations or process to analyse the financial information. This process is carried with some pre-decided objective and intentions. Usually it is done to assess performance and financial health of the organization or share and business valuation or capital project analysis or portfolio performance and risk assessment.
Financial modelling can be done with the help of developed software or it can be done manually through excel. The process or fix set of process as may be applicable to the desired objective is already designed and interlinked in the software or excel file for unknown variables. Once variables are inserted into to the model it will facilitate the desired output for intended objective.
Process or set of calculation will depend on various situation and objective and accordingly applicable tools will be used for financial modelling. Like for portfolio performance and risk assessment applicable tools will be CAPM model, Market model, intrinsic / fair value method, α, β, SML, SD, Correlation, covariance, probability etc.fcff_3 oct